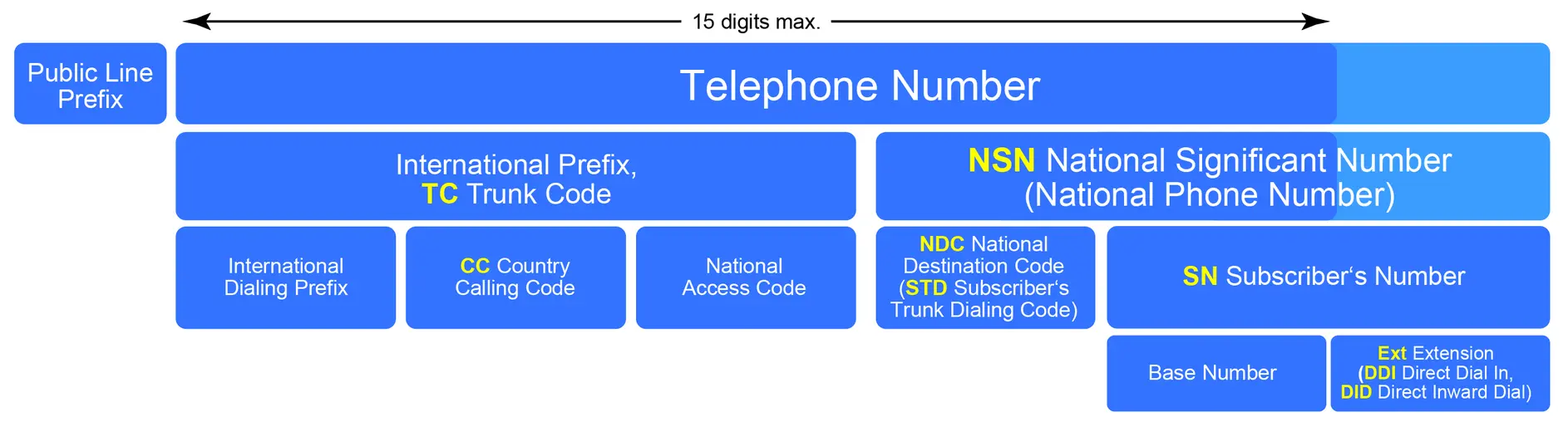
Telephone Number
A telephone number is a set of digits assigned to a fixed-line telephone subscriber station connected to a phone line, a wireless electronic telephony device, such as a radio telephone or a mobile telephone, or other devices for data transmission via the public switched telephone network (PSTN) or other public and private networks.
A telephone number is used as an address when employing a destination code routing scheme to transfer calls. A calling party enters or dials a telephone number on the originating telephone set, which transmits the sequence of digits to a telephone exchange as part of the signaling process.
The exchange connects the call to another locally connected subscriber or to the called party through the PSTN. Telephone numbers are allocated to customers by telephone service providers, which can be commercial companies, state-controlled administrations, or other telecommunication sector groups, as part of a national or regional telephone numbering scheme.
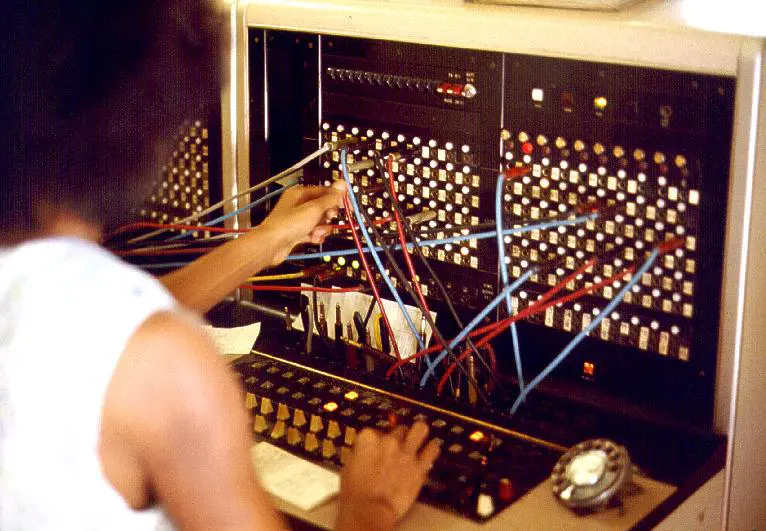

Historical Note
Telephone numbers were first used in Lowell, Massachusetts, in 1879, when callers connecting to the switchboard operator were asked for subscriber names. Telephone numbers have varied in length and structure throughout history, and even featured most letters of the alphabet in leading places when telephone exchange names were often used until the 1960s.
Telephone Numbering Plan
A telephone numbering plan is a sort of numbering scheme used in telecommunications to allocate phone numbers to subscriber phones and other telephony endpoints.
Geographic Considerations
Geographic location often plays a factor in the sequence of numbers issued to each telephone user in public numbering systems. Many numbering plan administrators split their service territory into geographic zones identified by a prefix, also known as an area code or city code.
Area Code
Telephone administrations that oversee large-scale telecommunication infrastructure, such as a country, frequently split the region into geographic divisions. This promotes autonomous control by administrative or historical subdivisions of the area or country, such as states and provinces.
Area Code Formats
- NANP (North America): 3 digits
- Brazil: 2 digits
- Australia/New Zealand: 1 digit
- Germany: 2-5 digits
- Japan: 1-5 digits
Country Code
Country codes are only required when calling numbers in countries different than the one from which the call originated. These numbers are called before the national number.
International Format
International phone numbers are displayed in listings by prefixing the country code with a plus sign (+). The subscriber is reminded to dial the international calling prefix for the country from which the call is made.
International Dialing Prefix
A trunk prefix used to choose an international telephone circuit for establishing an international call is known as an international call prefix or dial out code. It's currently known as an IDD prefix (international direct dialing), and each country has its own NDD prefix (national direct dialing).
ITU Standard
Most countries, but not all, have adopted the sequence 00 as a standard for an international call prefix, as recommended by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). The 00 prefix is used by some nations, followed by the international carrier code.